The content of the article:
- Concept and purpose of the oil pump
- Types (by the nature of management)
- Types of oil pumps (depending on the design)
- 1. Gear-type oil pump device
- 2. Rotary device
- 3. The principle of operation of the variable pump of the rotary type
- Scheme of the oil pump VAZ 2115, 2114 (Lada Samara)
Concept and purpose of the oil pump
An "oil" pump is a pump that puts pressure on the lubricant in the system, as a result of which all the moving parts of the internal combustion engine are provided with lubrication. In a dry sump, in addition to transporting lubricant, this part in the car also contributes to pumping oil from the engine crankcase to the oil tank.
The oil pump is driven by the crankshaft or the camshaft via the drive shaft.
Types (by the nature of management)
They can be combined into two groups, depending on the management features:
- Adjustable.
- Unregulated.
The former maintain a constant pressure in the lubrication system by adjusting the pump performance. In unregulated ones, the pressure does not change due to the action of the pressure reducing valve.
Types of oil pumps (depending on the design)
By design features, they can be:
- Rotary type (oil is transferred by the rotor blades).
- Gear type (oil is transmitted by gears).
The latter, in turn, are divided into two types by design: with external gearing (two gears are located near each other), and with internal gearing (one gear is in the other). If the performance of such pumps is the same, the overall dimensions of the internal gear pump are smaller than those of the external gear pumps, due to the location of the gears in one another.
1. Gear-type oil pump device

- driven gear
- suction channel
- pinion gear
- drive shaft
- discharge channel
- driven gear axle
The drive (first) and driven (second) gears are located in the pump housing. They transfer oil from the suction port through the discharge port to the system. Depending on the speed of the crankshaft, the performance of the oil gear pump changes in direct proportion. If the pressure of the discharged oil is higher than the permissible value determined for the pump, then part of the oil goes into the suction cavity or directly into the crankcase using a pressure reducing valve that is automatically triggered with an increase in pressure. belong to unregulated species.
2. Rotary device

- suction cavity
- butter
- outer rotor
- discharge cavity
- drive shaft
- inner rotor
The design of a rotary-type oil pump is a leading (inner) and driven (outer) rotors, placed in a housing.
In an unregulated rotary vane pump, the oil sucked in by the pump is pumped into the system through the rotor blades. When the pressure is exceeded, the pressure reducing valve also automatically works.
Unlike an unregulated pump, a rotary-type variable pump has a movable stator equipped with an adjusting spring to ensure constant pressure, regardless of the crankshaft speed. This movable stator controls the constant pressure by changing the volume of the cavity between the inner and outer rotors, turning the stator in the desired direction.
The advantages of a variable oil pump over an unregulated type are:
- Reducing the amount of power taken from the engine (up to 30%).
- Longer oil wear occurs due to a decrease in the speed, and therefore the number of revolutions.
- The oil does not foam as much as the unregulated type.
3. The principle of operation of the variable pump of the rotary type

A - Discharge side
B - Suction side
- discharge cavity
- outer rotor
- inner rotor
- adjusting spring
- suction cavity
- drive shaft
- movable stator
With acceleration of the crankshaft speed, the need for oil flow increases, as a result of which the pressure in the system decreases. The adjusting spring, responding to a decrease in pressure, drives the stator, which then acts on the driven rotor that touches it. As a result, the volume of the suction cavity decreases and, accordingly, the performance of the oil pump decreases.
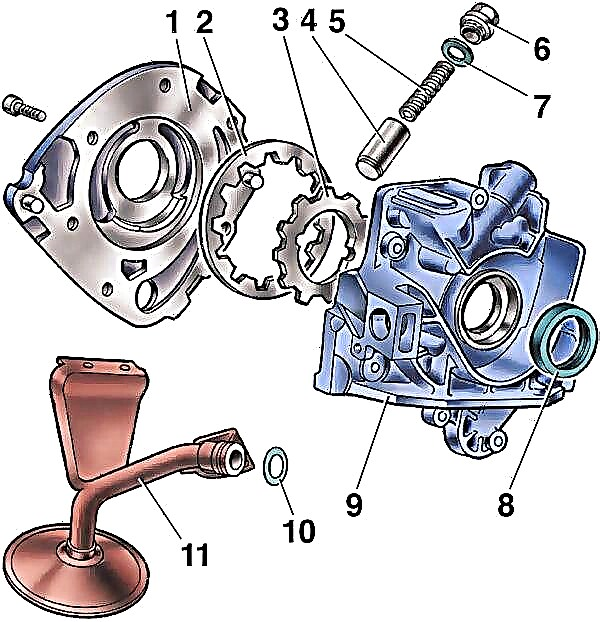
Scheme of the oil pump VAZ 2115, 2114 (Lada Samara)

- pump housing;
- driven gear;
- drive gear;
- pressure reducing valve;
- pressure relief valve spring;
- Cork;
- sealing ring;
- front crankshaft oil seal;
- pump cover;
- rubber sealing ring;
- oil receiver.
Honda Steed 400 Oil Pump Knock